AI Agents vs. LLMs: Why we need both in today’s world

We’re living through an interesting time in AI development. Every day, we see new tools and systems that promise to change how we work. But with all this innovation comes confusion about what these different technologies actually do. Two terms that come up constantly are “AI Agents” and “Large Language Models” (LLMs), and people often wonder if they’re the same thing or which one is better.
The truth is more nuanced than that. We need both, and here’s why.
LLMs: The conversation masters
Large Language Models like GPT-4, Claude, and others are essentially sophisticated text processors. They’ve been trained on enormous amounts of written content and can understand language patterns, generate responses, and help with various text-based tasks.
Think of an LLM as that really smart friend who knows a lot about everything and can explain complex topics clearly. When you ask ChatGPT to write an email, explain quantum physics, or help debug code, you’re tapping into this vast knowledge base.
What LLMs do well:
- They can follow long conversations and understand what you’re really asking for, even when you’re not being perfectly clear.
- From writing reports to creating code snippets, LLMs produce human-like text that’s often surprisingly good.
- They can summarize documents, translate languages, and analyze text in ways that would take humans much longer.
- LLMs have learned from diverse sources, making them useful generalists for many different topics.
But here’s where it gets interesting. LLMs are primarily conversational. They respond to what you ask them, but they don’t take initiative or perform actions in the real world.
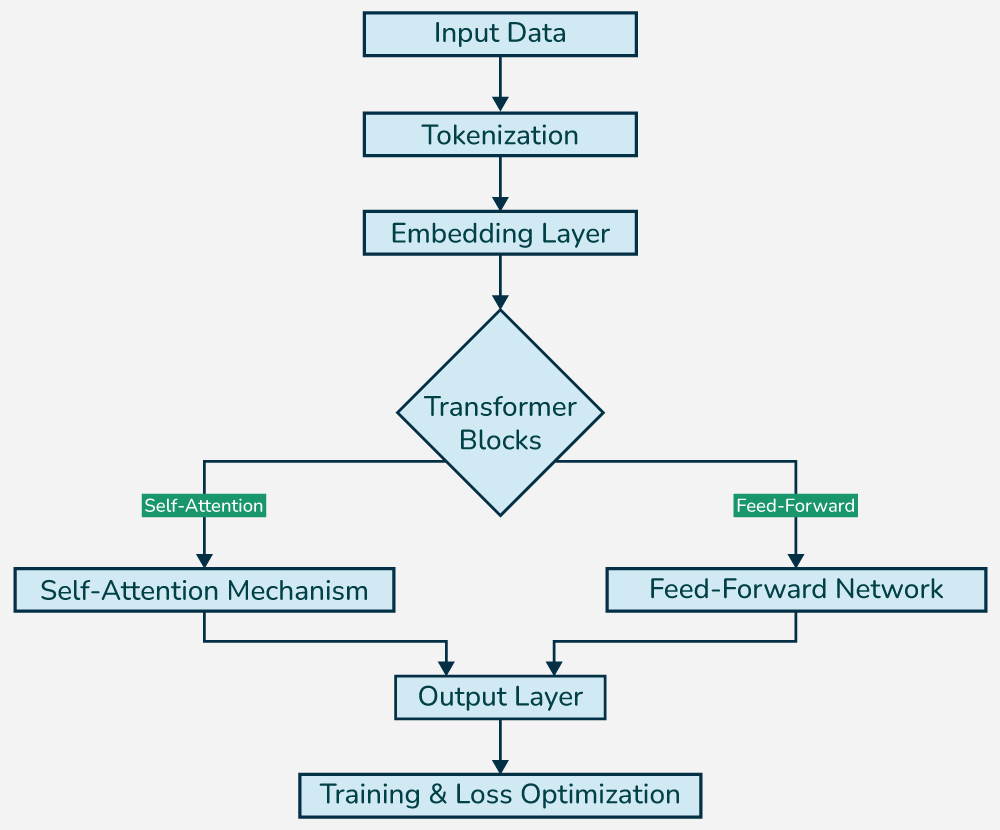
Credit: GeeksforGeeks
AI Agents: The autonomous workers
AI Agents represent a different approach entirely. While LLMs are great at conversation, Agents are designed to get things done independently. They can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals.
Imagine having a digital assistant who doesn’t just tell you how to book a restaurant reservation—they actually call the restaurant, check availability, and make the booking for you. That’s the difference we’re talking about.
What makes AI Agents different:
- Agents can interact with websites, send emails, update databases, and work with other software systems.
- Instead of just responding to immediate requests, Agents can break down complex tasks into steps and work through them systematically.
- Once you give an Agent a goal, it can work toward that goal without needing constant guidance.
- Many Agents can remember what worked before and adjust their approach based on past interactions.
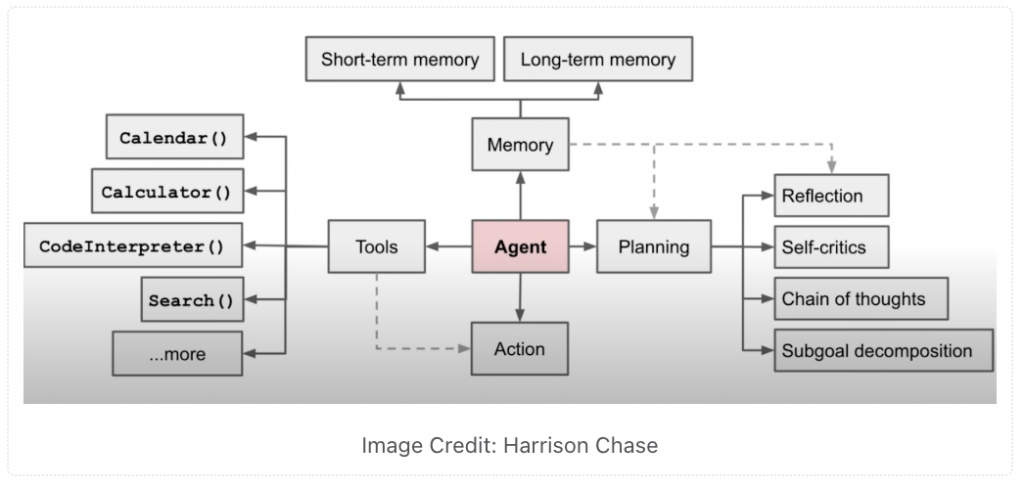
The spectrum of autonomy
Here’s something important that often gets missed: AI systems exist on a spectrum of autonomy. It’s not just “LLM or Agent”—there are different degrees of how much an AI system can act independently.
At one end, you have simple LLM applications that respond to prompts. In the middle, you might have systems that can route requests to different workflows or make simple decisions. At the other end, you have fully autonomous Agents that can use tools, remember long-term context, and work toward complex goals over extended periods.
Most practical AI applications today fall somewhere in the middle of this spectrum, combining the language understanding of LLMs with varying degrees of autonomous behavior.
AI Agents vs. LLMs: Why does the confusion exist?
Part of the confusion comes from the fact that many modern AI Agents actually use LLMs as their “brain” for reasoning and communication. So when you interact with an advanced AI Agent, you’re often seeing LLM capabilities enhanced with action-taking abilities.
It’s like the difference between having a brilliant consultant who can give you advice (LLM) versus having a brilliant assistant who can also go out and execute on that advice (LLM-powered Agent).
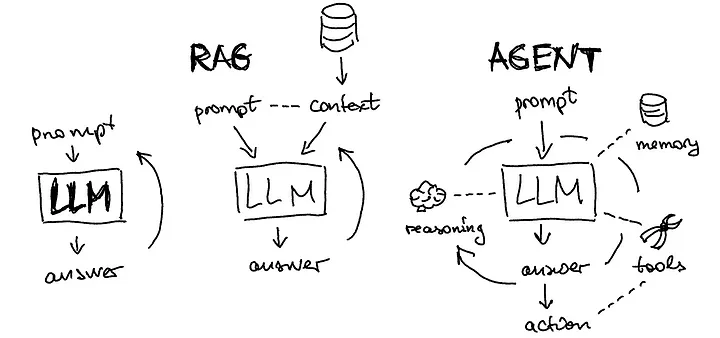
Credit: Medium
Real-world applications show the difference
The distinction becomes clearer when you look at actual use cases:
LLM applications excel at:
- Content creation and writing assistance
- Research and analysis
- Language translation
- Educational tutoring
AI Agent applications shine for:
- Customer service that can resolve issues. For reference, check out the AI CS Agent
- Personal assistants that manage your calendar and communications. For reference, check out the Cold Email AI Agent
- Trading systems that monitor markets and execute transactions
- Workflow automation that adapts to changing conditions. For reference, check out the HR process AI Agent
- Multi-step research projects that require gathering information from multiple sources
Technical considerations that matter
When deciding between LLM-based and Agent-based approaches, several practical factors come into play:
Complexity and maintenance: AI Agents are generally more complex to build and maintain. They need to handle errors, manage state across interactions, and integrate with multiple systems.
Predictability: LLMs tend to be more predictable in their outputs, while Agents may exhibit unexpected behaviors as they navigate complex scenarios.
Resource requirements: Agents often need more computational resources and infrastructure, especially when they’re running continuously or handling multiple tasks simultaneously.
Monitoring and control: With LLMs, you can easily see the input and output. With Agents, you need systems to monitor their actions and ensure they’re behaving as intended.
Looking ahead: AI Agents vs. LLMs
The boundary between LLMs vs. AI Agents continues to blur as both technologies evolve. We’re moving toward a future where:
- LLMs become more capable of taking actions and using tools
- AI Agents become better at reasoning and communication
- Hybrid systems become the standard approach
- Integration between different AI capabilities becomes seamless
But understanding the fundamental differences remains important for making good decisions about which approach fits your specific needs. At Tars, we are helping people build AI Agents driven by LLMs in combination with memory, tools, and prompting. With tooling capabilities, configuration options, an easy no-code building approach, and knowledge ingestion, we aim to help people automate their workflows.
The bottom line
We don’t think the question should be “AI Agent or LLM?” but rather “How can we use both effectively?”
LLMs excel at understanding, reasoning, and communicating. AI Agents excel at taking action, working independently, and integrating with complex systems. The most powerful AI applications we’re seeing today combine both capabilities thoughtfully. With Tars, you can easily build powerful and reliable AI Agents.
Whether you’re building AI solutions for your business or just trying to understand how these technologies can help you, the No-Code builder with the visual drag-and-drop canvas makes Agent building accessible for everyone. Just sign up, build, and automate!
A writer trying to make AI easy to understand.
- LLMs: The conversation masters
- What LLMs do well:
- AI Agents: The autonomous workers
- What makes AI Agents different:
- The spectrum of autonomy
- AI Agents vs. LLMs: Why does the confusion exist?
- Real-world applications show the difference
- Technical considerations that matter
- Looking ahead: AI Agents vs. LLMs
- The bottom line


Build innovative AI Agents that deliver results
Get started for freeRecommended Reading: Check Out Our Favorite Blog Posts!

10 best alternatives to Intercom (Fin AI) for AI-powered customer service [2025]

Customer experience automation: The complete guide to CXA in 2025

How to measure customer experience: The complete guide for AI-powered support and growth

Our journey in a few numbers
With Tars you can build Conversational AI Agents that truly understand your needs and create intelligent conversations.
years in the conversational AI space
global brands have worked with us
customer conversations automated
countries with deployed AI Agents



